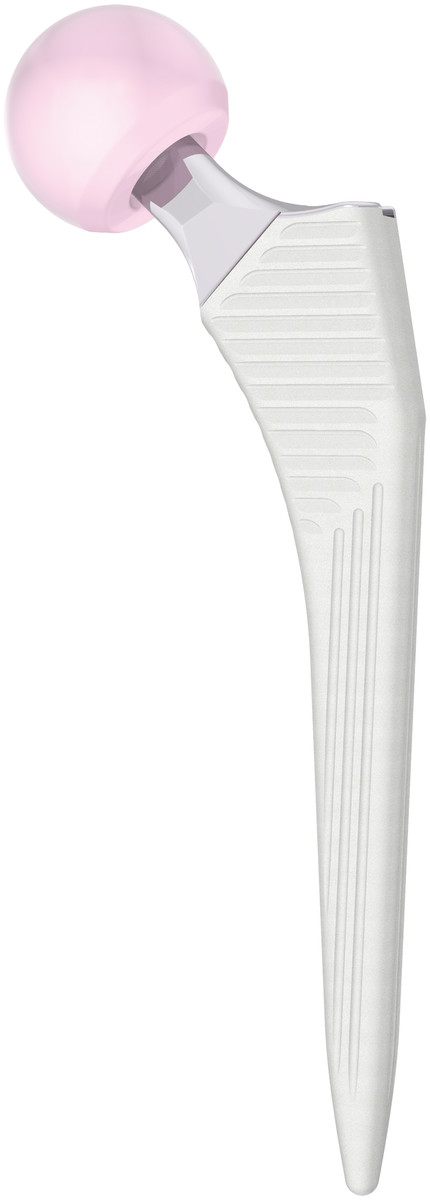
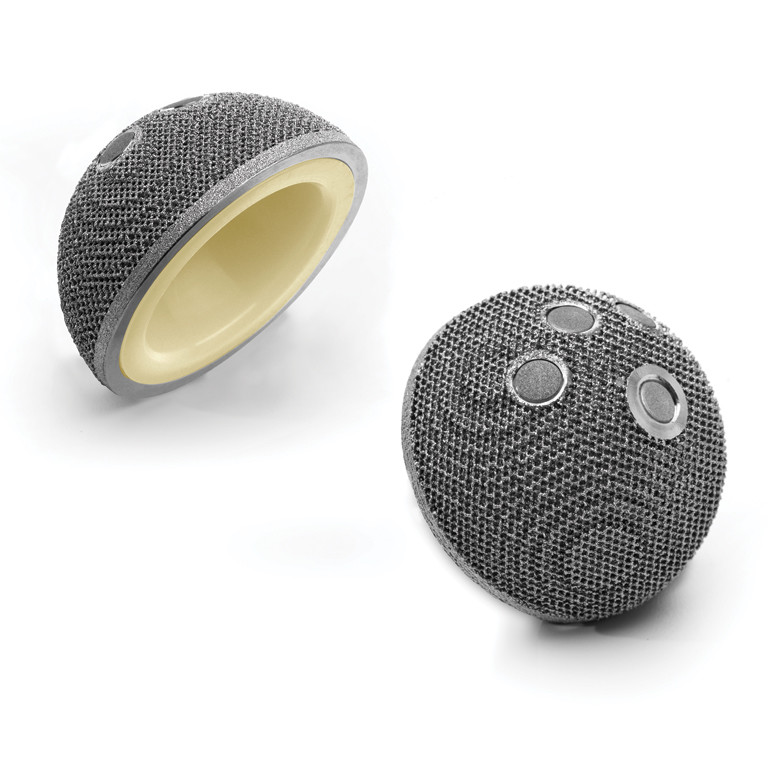
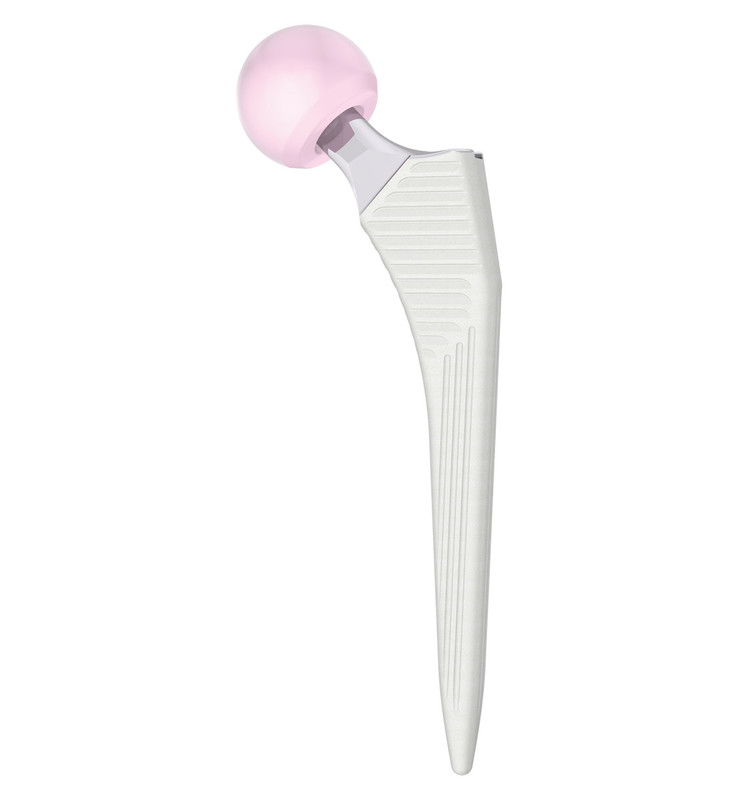
H-MAX S
The LimaCorporate H-MAX S builds on a trusted design with extra features and an optimised coating for enhanced biological fixation and natural offset distribution.
Benefits

01
Clinically proven promise of long-term survivorship
02
Full biological fixation enhanced by secondary stability
03
Real intraoperative versatility
3D View
Images

About
LimaCorporate’s H-MAX stem covers all surgical approaches from the most traditional to modern tissue-sparing techniques.
The low profile lateral shoulder design enables easy insertion in reduced incision techniques, especially the anterior approach. The H-MAX stem develops the principles of ‘Corail’ Philosophy: straight stem with rectangular cross section and with HA coting for an effective osteointegration.
See bibliography
BIBLIOGRAFIA
[1] Müller M, Tohtz S, Springer I, Dewey M, Perka C. Randomized controlled trial of abductor muscle damage in relation to the surgical approach for primary total hip replacement: minimally invasive anterolateral versus modifi ed direct lateral approach. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(2):179-89.
[2] D’Arrigo C, Speranza A, Monaco E, Carcangiu A, Ferretti A. Learning curve in tissue sparing total hip replacement: comparison between different approaches. J Orthop Traumatol. 2009;10(1):47-54.
[3] Pfl üger G, Junk-Jantsch S, Schöll V. Minimally invasive total hip replacement via the anterolateral approach in the supine position. Int Orthop. 2007;31(Suppl 1):7–11.
[4] Søballe K., Overgaard S. The current status of hydroxyapatite coating of prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Br; 1996;78(5):689-91.
[5] Lima Internal Report n° 2012.
[6] Røkkum M, Reigstad A, Johansson CB. HA particles can be released from well-fi xed HA-coated stems. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica. 2002;73(3):298-306.
[7] Dumbleton J, Manley MT. Hydroxyapatite-Coated Prostheses in Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(11):2526-40.
[8] Capello WN, D’Antonio JA, Jaffe WL, Geesink RG, Manley MT, Feinberg JR. Hydroxyapatite-coated Femoral Components. 15-Year Minimum Follow-up. Clinical Orthopaedic and Related Research. 2006;453:75–80.
[9] Charles MN, Bourne RB, Roderick Davey J, Greenwald A S, Morrey B F, Rorabeck CH. Soft Tissue balancing of the hip - The role of femoral offset restoration. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(5): 1078-88.
[10] Sakai T, Sugano N, Nishii T, Haraguchi K, Ochi T, Ohzono K. Optimizing femoral anteversion and offset after total hip arthroplasty, using a modular femoral neck system: an experimental study. Journal of Orthopaedic Science. 2000;5(5):489-94.
[11] Fusi S, Paris D, Dalla Pria P, Bloch HR, Pressacco M. L’evoluzione del disegno protesico dei colli modulari: lo stelo H-MAX M. Sphera Medical Journal. 2009 ;10:60-3.
[12] Lima Internal Report n° 2008-03.
[1] Müller M, Tohtz S, Springer I, Dewey M, Perka C. Randomized controlled trial of abductor muscle damage in relation to the surgical approach for primary total hip replacement: minimally invasive anterolateral versus modifi ed direct lateral approach. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(2):179-89.
[2] D’Arrigo C, Speranza A, Monaco E, Carcangiu A, Ferretti A. Learning curve in tissue sparing total hip replacement: comparison between different approaches. J Orthop Traumatol. 2009;10(1):47-54.
[3] Pfl üger G, Junk-Jantsch S, Schöll V. Minimally invasive total hip replacement via the anterolateral approach in the supine position. Int Orthop. 2007;31(Suppl 1):7–11.
[4] Søballe K., Overgaard S. The current status of hydroxyapatite coating of prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Br; 1996;78(5):689-91.
[5] Lima Internal Report n° 2012.
[6] Røkkum M, Reigstad A, Johansson CB. HA particles can be released from well-fi xed HA-coated stems. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica. 2002;73(3):298-306.
[7] Dumbleton J, Manley MT. Hydroxyapatite-Coated Prostheses in Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(11):2526-40.
[8] Capello WN, D’Antonio JA, Jaffe WL, Geesink RG, Manley MT, Feinberg JR. Hydroxyapatite-coated Femoral Components. 15-Year Minimum Follow-up. Clinical Orthopaedic and Related Research. 2006;453:75–80.
[9] Charles MN, Bourne RB, Roderick Davey J, Greenwald A S, Morrey B F, Rorabeck CH. Soft Tissue balancing of the hip - The role of femoral offset restoration. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(5): 1078-88.
[10] Sakai T, Sugano N, Nishii T, Haraguchi K, Ochi T, Ohzono K. Optimizing femoral anteversion and offset after total hip arthroplasty, using a modular femoral neck system: an experimental study. Journal of Orthopaedic Science. 2000;5(5):489-94.
[11] Fusi S, Paris D, Dalla Pria P, Bloch HR, Pressacco M. L’evoluzione del disegno protesico dei colli modulari: lo stelo H-MAX M. Sphera Medical Journal. 2009 ;10:60-3.
[12] Lima Internal Report n° 2008-03.
Sizing
& Options
Resources
Disclaimer
Please note that not all products are available and registered in every market. Please contact your LimaCorporate Sales Representative for any further information.
LPSI, SpaceFlex e SYMBOL® are distributed by Limacorporate S.p.A.
BIOLOX® / BIOLOX®delta / BIOLOX OPTION® is a registered trademark of a company of the CeramTec Group, Germany.
LPSI, SpaceFlex e SYMBOL® are distributed by Limacorporate S.p.A.
BIOLOX® / BIOLOX®delta / BIOLOX OPTION® is a registered trademark of a company of the CeramTec Group, Germany.